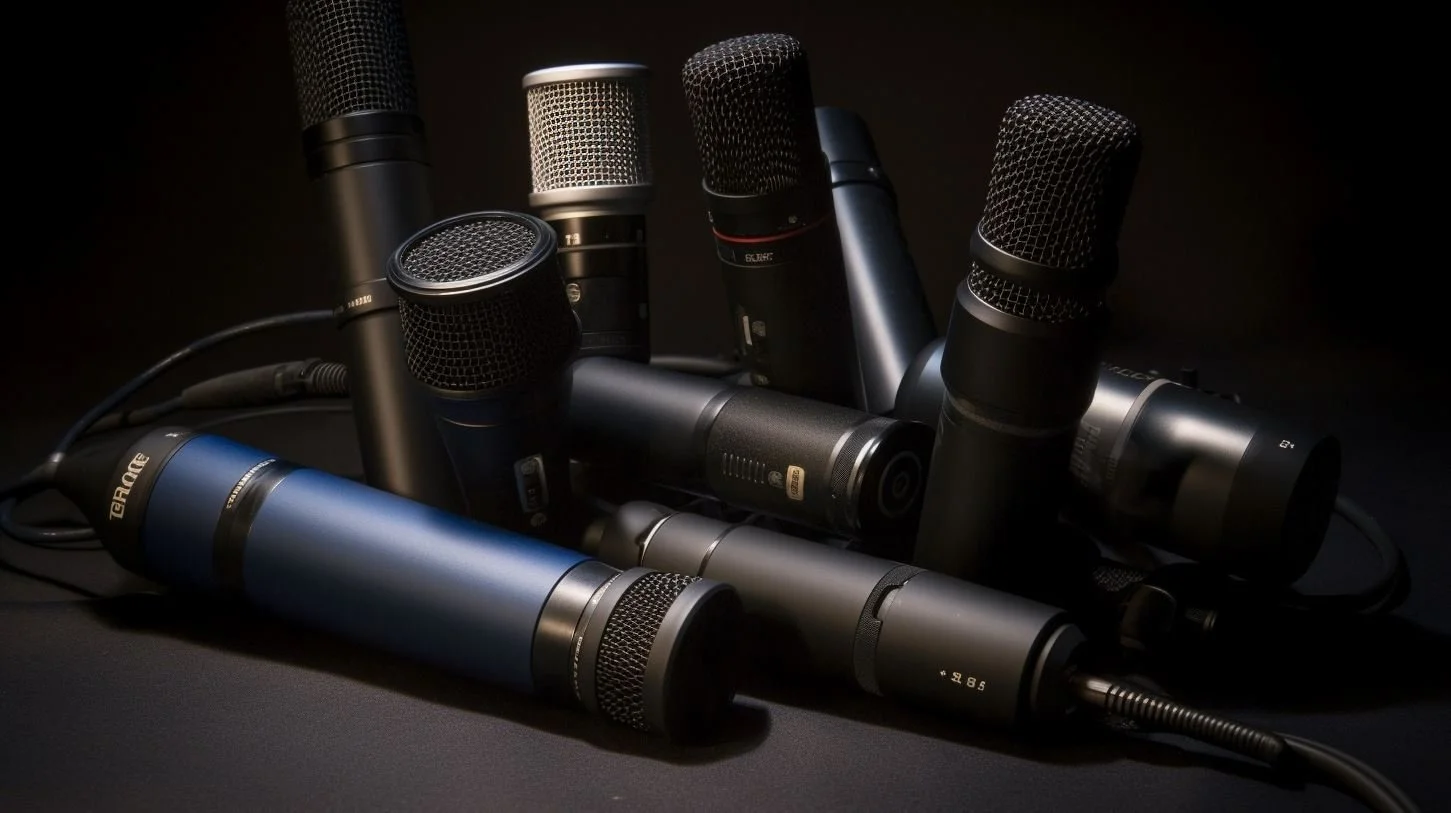
Best Omnidirectional Microphone
Capturing Sound from Every Angle: The Top Picks in Omnidirectional Microphones
Navigating the world of omnidirectional microphones can feel like diving deep into a rich sonic universe.
With the plethora of options available, pinpointing the perfect one for your specific needs and budget can be a daunting task.
We've embarked on this audio journey, sorted through the noise, and curated an ultimate buyer's guide to simplify your decision-making process.
Whether you're a podcaster, a filmmaker, an interviewer, or simply someone who demands pristine audio clarity, we've got you covered.
To help you in your audio pursuits, we've handpicked six outstanding omnidirectional microphones across various price points and functionalities.
These top contenders promise to deliver impeccable performance, ensuring your sounds are captured with precision, clarity, and fidelity.
Disclaimer: This blog post contains affiliate links. If you make a purchase through one of these links, we may receive a small commission at no additional cost to you. This helps support our work and allows us to continue providing valuable content. Thank you for your support!
Read Before Buying:
Due to the 360° sound capture of omnidirectional microphones, they’re most commonly used to record ambient environments.
These spaces tend to be relatively quiet, so choosing an omnidirectional microphone with low noise is essential for optimal sound quality.
What is microphone noise?
All microphones produce a static hissing sound when turned on (self-noise). The amount of noise varies (and you usually get what you pay for), but even the most advanced microphones have some level of self-noise.
The key is to choose an omnidirectional microphone that’s quiet enough to record your sounds without having the background hiss of the microphone audible in the final recording.
In my professional experience recording quiet nature sounds, I’ve found that you need your microphone to be at least 20dB quieter than the sounds you want to record for best results.
For example, ambient bird song is around 30dB in loudness so you would want a microphone that has 10dB of self-noise or less for best results.
Conversely, recording a human conversation, like an interview, has an average loudness of 60dB, so you could afford to use a “louder” microphone with a self-noise around 40dB
To help you decide what your microphone self-noise needs are, please see the decibel diagram below:
Quick Links:
Below are our top picks for the best omnidirectional microphones based on self-noise, price, and popularity:
Omnidirectional Microphone Top-Picks:
Best Budget: sE Electronics sE8 - High-quality, low-noise omnidirectional microphones complete with essential accessories for reliable recording.
Best Value: Audio Technica AT4022 - An efficient, low-noise omnidirectional microphone, favored by nature recordists for its value.
Best Overall: Sennheiser MKH 8020 - Industry-leading low noise with added moisture resistance, ensuring consistent recordings even in high humidity.
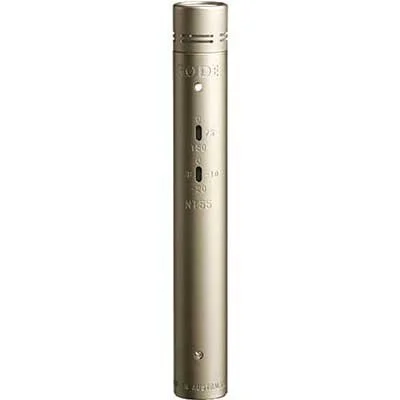
Most Versatile: Rode NT55 - Versatile microphone with interchangeable omnidirectional and cardioid capsules suitable for diverse recording scenarios.
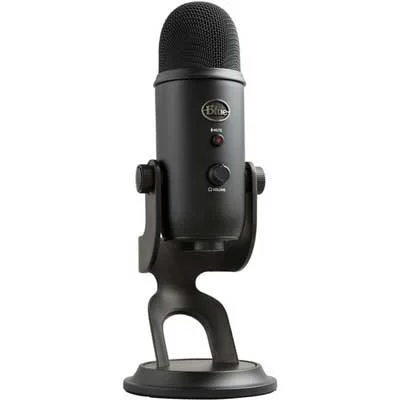
For Streaming/Interviews: Blue Yeti - Optimal for streaming and interviews, this microphone offers clear speech recording with multiple polar pattern options.
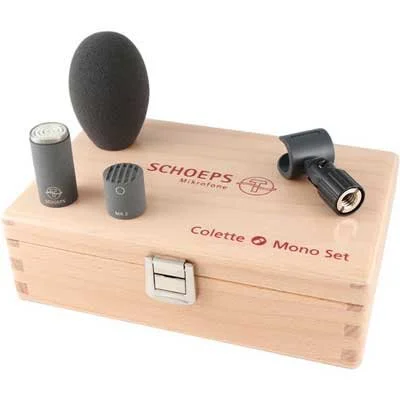
Premium Option: Schoeps CMC 1 MK 2 - A premium microphone renowned for superior sound quality, albeit lacking moisture resistance at its price point.
Best Omnidirectional Microphone
(sorted by price from ↓↑)
Best Budget
sE Electronics sE8
A phenomenal deal for a pair of low-noise omnis. Includes stereo bar, mic clips, hard case, and foam windscreens.
| Self-Noise: | 15 dBA |
| Sensitivity: | -34 dB |
| Output: | XLR |
| Power: | 48V |
Best Value
Audio Technica AT4022
Very low-noise omnidirectional microphone at an unbeatable price. Very popular with nature recordists.
| Self-Noise: | 13 dBA |
| Sensitivity: | -34 dB |
| Output: | XLR |
| Power: | 48V |
Best Overall
Sennheiser MKH 8020
The lowest noise omni on the market with moisture resistance for worry-free recordings in high humidity.
| Self-Noise: | 10 dBA |
| Sensitivity: | -30 dB |
| Output: | XLR |
| Power: | 48V |
Most Versatile
Rode NT55
Includes interchangeable omnidirectional and cardioid capsules for a wide range of sonic scenarios.
| Self-Noise: | 15 dBA |
| Sensitivity: | -38 dB |
| Output: | XLR |
| Power: | 48V |
For Streaming/Podcasts
Blue Yeti
An extremely popular and affordable option for recording human speech.
| Noise Floor: | N/A |
| Sensitivity: | N/A |
| Output: | USB-A |
| Power: | Bus Power |
Premium Option
Schoeps CMC 1 MK 2
Touted as the premier sound quality manufacturer. Would like to see moisture resistance at this pricepoint.
| Noise Floor: | 10 dBA |
| Sensitivity: | -35.5 dB |
| Output: | XLR |
| Power: | 48V |
What Is an Omnidirectional Microphone?
The term "omnidirectional" can be broken down to understand its core meaning. "Omni" means "all," and "directional" pertains to direction. Thus, an omnidirectional microphone is designed to capture sound from all directions equally. This contrasts with other types like the cardioid microphone, which primarily captures sound from the front.
The Working Principle
Omnidirectional spherical pickup pattern.
The sensitivity pattern of a microphone dictates from which direction it captures sound most effectively.
In the case of omnidirectional microphones, this sensitivity is uniform in all directions, forming a perfect sphere around the microphone.
This means whether sound originates from the front, sides, or even behind the microphone, it will be captured with the same intensity.
Key Advantages
1. Consistent Sound Capture: Omnidirectional microphones excel in environments where sound sources move or where it's difficult to pinpoint a single direction of sound. They ensure that all sounds, from every direction, are consistently recorded.
2. Less Handling Noise: These microphones tend to be less sensitive to handling noise or wind noise, making them ideal for scenarios like handheld interviews or outdoor recordings.
3. Versatile in Group Settings: In situations like a roundtable discussion or a group interview, where participants are seated around the microphone, its 360-degree sound capture ensures that everyone's voice is equally represented.
Limitations to Consider
1. Background Noise: Since omnidirectional mics capture sound from all directions, they can't discriminate between the intended sound source and background noise. In noisy environments, this can be a drawback.
2. Lack of Directional Focus: In situations where the focus should be on a singular sound source, like in stage performances, an omnidirectional microphone might capture too much ambient noise or echo.
Ideal Use Cases
1. Conference Calls: They ensure that voices from all around the table are equally clear.
2. Field Recordings: For capturing the ambient sounds of an environment.
3. Choirs: To capture the collective sound without focusing on one particular section.
4. Interviews: Especially in quiet environments or when the direction of the sound source might change frequently.
Buyer’s Guide to Binaural Microphones for ASMR
Selecting the best omnidirectional microphone is not merely about choosing a brand or model; it's about understanding the specific needs of your project and how different microphones can meet those needs.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through the key aspects to consider when making a purchase.
1. Understand Your Requirement:
Before diving into the world of omnidirectional microphones, take a moment to consider your primary application. Are you a podcaster, a field recorder, or someone recording roundtable discussions?
2. Budget:
Set a realistic budget. Omnidirectional microphones range from very affordable to professional-grade high-end models. Your budget will largely determine the range of products available for your consideration.
3. Sound Quality:
While all omnidirectional microphones have the inherent quality of capturing sound from all directions, the clarity, warmth, and fidelity can vary.
Frequency Response: Look for a microphone with a broad frequency response, ensuring it captures both low and high frequencies adequately.
-
When selecting the perfect omnidirectional microphone, understanding frequency response is paramount. This guide will break down what frequency response is, why it matters, and how to discern the nuances when making your purchase.
1. Introduction to Frequency Response
Frequency response refers to the range of frequencies a microphone can accurately capture and reproduce, typically measured in Hertz (Hz) and expressed as a range, like 20Hz-20kHz.
2. Why It Matters
Sound Spectrum and Human Hearing: Humans generally hear sounds in the range of 20Hz (low bass) to 20kHz (high treble). A microphone with a frequency response that encompasses this range will likely reproduce most sounds we can hear.
Recording Fidelity: A broad and flat frequency response ensures that the recording closely matches the original sound, maintaining its natural timbre and nuances.
3. Reading Frequency Response Charts
A frequency response chart plots the microphone's sensitivity across its operational frequency range.
Flat Response: Indicates consistent sensitivity across all frequencies. This type of response is often desired for transparent recordings, such as in classical music.
Peaks & Dips: Highlight areas where the microphone boosts or cuts certain frequencies. This can color the sound in unique ways, which may be desirable for specific applications.
4. Considerations for Specific Applications
Vocals: For clear vocal recordings, prioritize a microphone that offers good response in the midrange frequencies (around 1kHz to 5kHz). A slight boost in the high frequencies can add clarity and presence.
Instruments: Depending on the instrument, you might need a mic with a particular frequency response. For instance, bass instruments like kick drums benefit from mics that capture lower frequencies well.
Ambient Sounds: If you're capturing the ambiance or nature sounds, a broad frequency response ensures you get both the low rumble and the high-frequency nuances.
5. Limitations of Frequency Response
While a broad frequency response is generally desirable, it doesn’t guarantee overall sound quality. Other factors like transient response, distortion, and noise floor can impact the audio quality.
6. Frequency Response and Directivity
Even if two omnidirectional microphones have similar frequency responses, their directivity can affect how they capture sound in real-world environments. Ensure the microphone's omnidirectional nature doesn't overly compromise frequency consistency from different sound sources.
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR): A higher SNR indicates that the microphone will capture more of your desired sound and less background noise.
-
In the world of audio, few parameters are as crucial yet overlooked as the Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR). When choosing an omnidirectional microphone, understanding SNR can make all the difference in achieving professional-quality recordings. Let's dive into the ins and outs of SNR and its relevance in microphone selection.
1. What is Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR)?
SNR measures the level of a desired signal (in this case, the audio you're recording) to the level of background noise. It's typically expressed in decibels (dB). A higher SNR value indicates that the signal is higher than the level of the noise, leading to clearer recordings.
2. Why SNR Matters
Clarity: A microphone with a high SNR ensures that your recordings have minimal background noise, resulting in clear and professional-quality audio.
Post-Production Flexibility: A recording with less noise provides more flexibility in post-production, allowing for enhancements without amplifying the noise floor.
3. Understanding SNR Values
In the realm of microphones:
Excellent SNR: Anything above 80dB is considered outstanding and will offer a pristine recording experience.
Good SNR: Ranges between 60dB to 80dB. Suitable for most professional applications.
Average SNR: 40dB to 60dB. Acceptable for many casual recordings but may require noise reduction in post-production.
4. External Factors Impacting SNR
While the microphone's inherent SNR is pivotal, external factors can also influence the effective SNR of a recording.
Environment: Recording in a quiet studio versus a bustling city street will impact the perceived SNR.
Mic Placement: Positioning the microphone closer to the sound source can help improve the effective SNR.
5. SNR in Omnidirectional Microphones
Given the nature of omnidirectional microphones to pick up sound from all directions, achieving a high SNR can be challenging. However, premium omnidirectional microphones are engineered to maintain a high SNR even with their 360-degree sound capture.
6. Comparing with Other Specs
While SNR is crucial, it's just one piece of the puzzle. It's essential to look at SNR in conjunction with other specs like frequency response, sensitivity, and max SPL to ensure a well-rounded microphone performance.
4. Build Quality:
For those always on the move or often working in rugged environments, a durable build is crucial. Metal constructions tend to last longer than plastic ones.
-
When evaluating omnidirectional microphones, while performance metrics like frequency response and SNR are vital, the build quality cannot be ignored. A microphone's build quality can greatly impact its longevity, reliability, and performance. In this guide, we'll explore what constitutes excellent build quality and how to identify it.
1. Why Build Quality Matters
Durability: A robustly built microphone ensures long-lasting performance, even in challenging environments or frequent use.
Performance Stability: Build quality directly influences the microphone's consistent performance. A well-constructed mic is less likely to develop unexpected issues or changes in sound quality over time.
Value for Money: While high build quality may come with a higher price tag initially, the long-term reliability often translates to better value over the microphone's lifespan.
2. Materials Used
Metal vs. Plastic: While metal-bodied microphones often offer more durability than plastic counterparts, advanced polymers used in some high-quality mics can be equally resilient.
Mesh Grill: Look for hardened steel or similar durable materials that protect the microphone's capsule without compromising sound clarity.
Internal Components: The quality of the internal electronics, wiring, and diaphragm material also plays a crucial role in the microphone's overall build quality and performance.
3. Construction Techniques
Solid Assembly: The best microphones feel solid in hand, with no rattling or loose components. Every part, from screws to connectors, should be firmly in place.
Reinforced Connectors: Since connectors can undergo wear and tear with frequent plugging and unplugging, premium microphones often feature reinforced XLR or USB connectors.
4. Environmental Protection
Moisture Resistance: Some microphones, especially those designed for outdoor use, feature moisture-resistant designs or materials to prevent damage from humidity or accidental splashes.
Dust and Debris: A tightly constructed microphone can prevent minute particles from entering and damaging internal components.
5. Design Ergonomics
While not strictly a durability factor, the design's ergonomics can indicate a well-thought-out microphone. Comfortable grip, balanced weight distribution, and intuitive placement of controls all point to meticulous design and build processes.
5. Connectivity:
Microphones come with various connectivity options:
XLR: Ideal for professional setups and offers the best sound quality.
USB: Great for podcasters or streamers who want to connect directly to a computer.
3.5mm: Suitable for casual recording or connection to consumer-grade cameras and recorders.
-
In today's digital age, the way your omnidirectional microphone connects to recording devices, be it computers, audio interfaces, or portable recorders, plays a crucial role in its versatility and usability. In this guide, we'll deep dive into the world of microphone connectivity, helping you choose the best option tailored to your needs.
1. Why Connectivity Matters
Versatility: Your microphone's connectivity determines the range of devices it can interface with.
Signal Quality: Different connection types can influence audio signal quality and the need for additional equipment.
Ease of Use: Some connectivity options are plug-and-play, while others may require additional setup or drivers.
2. XLR Connectivity
Overview: The XLR connector is a staple in professional audio. Typically featuring three pins, it provides a balanced audio signal, reducing the chance of interference.
Best For: Studio recording setups, live sound, and professional applications where sound quality and reliability are paramount.
Considerations: Most XLR microphones require an audio interface or mixer to connect to a computer or recording device. They might also need external power sources, like phantom power.
3. USB Connectivity
Overview: USB microphones convert analog signals to digital within the microphone itself and can be plugged directly into a computer.
Best For: Podcasters, streamers, and on-the-go recording setups. They're typically plug-and-play, making them user-friendly for beginners.
Considerations: While incredibly convenient, some USB mics may not offer the same audio quality as professional XLR counterparts. However, high-end USB mics can challenge this norm.
4. 3.5mm (1/8") Connectivity
Overview: These connectors are often found on consumer-grade microphones and can plug directly into many cameras, recorders, and computers.
Best For: Casual recording, video conferencing, and basic content creation.
Considerations: Due to their unbalanced nature, these connectors may be more susceptible to interference over longer cable lengths compared to XLR.
5. Wireless Connectivity
Overview: Wireless microphones transmit audio without physical cables, using frequencies like UHF or VHF, or digital transmission methods.
Best For: Stage performances, interviews, and scenarios where mobility without the hindrance of cables is essential.
Considerations: Consider battery life, range, and potential interference. It's also vital to check local regulations regarding wireless frequency usage.
6. Digital Interfaces (Lightning, USB-C, etc.)
Overview: Some modern microphones connect directly to smartphones or tablets using digital connectors like Lightning (for Apple devices) or USB-C.
Best For: Mobile journalism, on-the-spot interviews, and content creators leveraging mobile devices.
Considerations: Ensure compatibility with your device. Some might require additional adapter cables.
7. MIDI Connectivity
While less common for traditional microphones, some specialized mics, especially those used for electronic music production, may offer MIDI connectivity to interface with synthesizers or digital audio workstations.
8. Multi-Connectivity Options
Some advanced microphones come with multiple connection options, such as XLR combined with USB outputs, offering users flexibility based on their setup.
9. Cable Quality
Regardless of the connector type, the cable's quality can influence signal integrity. Opt for shielded cables from reputable brands to reduce interference and enhance durability.
10. Future-Proofing Your Purchase
With the rapid evolution of technology, considering future connectivity trends can be a smart move. For instance, as more devices embrace USB-C, investing in a microphone with this connection (or adapters) can be forward-thinking.
6. Portability:
If you're a field recorder or a journalist, the size and weight of the microphone matter. Compact and lightweight models are preferable.
-
In an era defined by mobility and on-the-go content creation, portability has risen as a key factor when selecting an omnidirectional microphone. From vlogging to impromptu music sessions, the need for compact, lightweight, yet powerful microphones has never been more pronounced. This guide will steer you through the nuances of portability in omnidirectional microphones.
1. Why Portability Matters
On-The-Go Recording: For journalists, vloggers, and podcasters, a portable microphone ensures you're always ready to capture high-quality audio, wherever inspiration strikes.
Travel-friendly: Portable mics are generally designed to be robust and travel-friendly, ensuring durability during transport.
Space Efficiency: For those with limited studio space, portable microphones can be easily stowed away after use.
2. Size and Weight
Compact Design: The most obvious factor in portability is the microphone's size. Opt for mics designed to be compact without compromising on sound quality.
Lightweight Materials: Advanced polymers and certain metals can offer a balance between durability and weight.
7. High-Pass Filters:
High-pass filters allow high-frequency sounds to pass through while attenuating lower frequencies. This is beneficial for eliminating unwanted low-frequency noises, such as rumblings or wind.
-
Within the realm of professional audio recording, having a built-in high pass filter (HPF) in an omnidirectional microphone can significantly enhance the recording quality. For those new to the terminology or looking to understand its significance, this guide will explain the what, why, and how of built-in high pass filters in omnidirectional microphones.
1. What is a High Pass Filter?
A high pass filter, also known as a low cut filter, is an electronic filter that allows frequencies above a specified cutoff point to pass through while reducing the lower frequencies. In the context of a microphone, this means attenuating frequencies that are below a certain threshold.
2. Why High Pass Filters Matter
Eliminate Low-Frequency Noise: Omnidirectional microphones, by design, pick up sound from all directions. An HPF can help reduce unwanted low-frequency sounds like traffic rumble, air conditioning hum, and handling noise.
Avoid Wind Noise: For outdoor recordings, wind noise can be a prominent issue. An HPF helps in minimizing this disturbance.
Enhanced Clarity: By removing low-frequency sounds, recordings often sound clearer and more focused on the desired audio source.
3. Fixed vs. Adjustable HPF
Fixed HPF: Some microphones come with a preset high pass filter frequency, which is activated by a switch.
Adjustable HPF: More versatile microphones offer adjustable HPFs, allowing users to select the cutoff frequency based on their recording needs.
4. HPF Activation Mechanism
Most modern omnidirectional microphones equipped with HPFs have an easily accessible switch or knob. Ensure that this switch is robust and doesn't introduce noise when activated during a recording session.
5. Frequency Threshold
Different recording scenarios require different HPF thresholds. Understanding the frequency range of the unwanted noise can help in selecting a microphone with an appropriate HPF setting. Common thresholds include 80Hz and 120Hz, but more advanced microphones might offer a wider range.
6. Slope Consideration
The steepness or slope of an HPF dictates how rapidly frequencies below the cutoff are attenuated. This is often measured in decibels per octave (dB/oct). A steeper slope provides a more aggressive filter.
7. Sound Character Preservation
While an HPF is beneficial, it's essential that activating it doesn't compromise the natural sound character of the microphone. Premium omnidirectional microphones ensure that the filter's introduction retains the overall audio quality.
8. Context of Use
For studio recordings in controlled environments, a strong HPF might not be as crucial. However, for field recordings, interviews in varied locations, or any outdoor recording, an HPF can be indispensable.
9. HPF in Post-Production
While having an HPF on the microphone is advantageous, it's also worth noting that high pass filtering can be applied during post-production using audio editing software. However, a built-in HPF provides real-time results and can be more efficient.
8. Attenuation Pads:
These pads reduce the microphone's sensitivity, allowing it to handle higher sound pressure levels (SPL) without distortion. This is particularly useful when recording loud sound sources.
-
Amid the vast features that modern omnidirectional microphones boast, the built-in attenuation pad switch stands out as a vital tool for various recording scenarios. For those contemplating the significance of this feature and wondering if it's worth the investment, this guide dives deep into the world of built-in attenuation pad switches in omnidirectional microphones.
1. What is an Attenuation Pad Switch?
An attenuation pad switch, often simply referred to as a "pad," is a feature on a microphone that reduces the input level or sensitivity. In essence, when activated, it allows the microphone to handle higher sound pressure levels (SPL) without distorting.
2. Why Attenuation Pad Switches Matter
Handling Loud Sources: Whether you're recording a blaring guitar amplifier, booming drums, or a passionate speaker, an attenuation pad ensures the microphone captures the sound without distortion.
Versatility: With a pad switch, a single microphone becomes suitable for a broader range of recording environments and sound sources.
Protecting Equipment: Overloading a microphone can harm both the microphone and connected equipment. An attenuation pad helps avoid potential damage.
3. Common Attenuation Levels
Attenuation pad switches usually offer a reduction in sensitivity by a set number of decibels (dB), such as -10dB, -15dB, or -20dB. Some microphones provide multiple pad options, allowing users to select the best level of reduction for the situation.
4. Switch Placement and Durability
A well-designed pad switch should be easily accessible yet robust. It shouldn't be easily triggered accidentally, but it should withstand regular use without wear and tear.
9. Moisture Resistance:
RF biased microphones are designed to handle moisture better, making them suitable for outdoor recordings or humid environments. These microphones use an RF voltage to polarize the microphone's capsule, reducing the adverse effects of moisture.
-
Whether you're a filmmaker braving the elements, a sports commentator at the mercy of unpredictable weather, or an adventurer documenting tales from the wilderness, moisture resistance—especially RF biased technology—in omnidirectional microphones is a critical consideration. Dive into this guide to navigate the wet and wild world of moisture-resistant omnidirectional mics.
1. What is RF Biased Technology?
RF (Radio Frequency) biased microphones utilize an electronic circuit to create an RF voltage, which is then applied to the microphone's capsule. This RF voltage is largely immune to moisture, making RF biased microphones particularly resilient in humid or wet environments.
2. Why Moisture Resistance Matters
Protecting the Equipment: Moisture can corrode internal components, shortening the microphone's lifespan.
Maintaining Sound Quality: Moisture can cause a drop in sound quality, introducing pops, crackles, or complete signal loss.
Versatility: A moisture-resistant microphone ensures consistent performance across various environments, from humid studios to rainy outdoor locations.
3. The Science Behind RF Biased Technology
Unlike traditional DC-biased microphones, RF biased models don't rely on a direct current. This makes them less sensitive to environmental factors, including temperature fluctuations and moisture. Their design ensures the capsule remains polarized even when wet, preventing short-circuiting and maintaining sound clarity.
10. Accessories:
Some microphones come bundled with essential accessories like pop filters, carrying cases, or boom arms. This can be both cost-effective and convenient.
-
While the microphone itself is undeniably the heart of any audio recording setup, the accessories accompanying it play a significant role in enhancing the overall experience and quality. From pop filters to carrying cases, each accessory contributes its own functionality. Let’s dive into the essential accessories you might consider when investing in an omnidirectional microphone.
1. Pop Filters and Windshields
Purpose: Pop filters (typically used indoors) minimize plosive sounds, such as 'p' and 'b', which can cause distortion. Windshields, often fluffy or foam covers, reduce wind noise during outdoor recordings.
Buying Tip: Ensure the pop filter or windshield is compatible with the size and design of your microphone. For outdoor enthusiasts, a windjammer—an advanced type of windshield—is a worthy investment.
2. Boom Poles and Stands
Purpose: These provide a means to hold or suspend the microphone, either stationary (like in a studio) or on the move (like in field recording or film shooting).
Buying Tip: For portability, opt for lightweight, collapsible boom poles. If stability is a priority, invest in a robust stand with a wide base.
3. Shock Mounts
Purpose: These isolate the microphone from vibrations and handling noise, ensuring cleaner recordings.
Buying Tip: A shock mount should fit the microphone snugly while effectively dampening vibrations. Some microphones come with custom shock mounts, but universal options are also available.
4. Carrying Cases and Storage Pouches
Purpose: Protect the microphone and accessories during transport and ensure they’re organized.
Buying Tip: Look for cases with padded interiors and compartments for different accessories. Waterproofing is a bonus for outdoor use.
6. Best Binaural Microphones for ASMR:
Below are our top picks for the best omnidirectional microphones based on self-noise, price, and popularity:
Omnidirectional Microphone Top-Picks:
Best Budget: sE Electronics sE8 - High-quality, low-noise omnidirectional microphones complete with essential accessories for reliable recording.
Best Value: Audio Technica AT4022 - An efficient, low-noise omnidirectional microphone, favored by nature recordists for its value.
Best Overall: Sennheiser MKH 8040 - Industry-leading low noise with added moisture resistance, ensuring consistent recordings even in high humidity.
Most Versatile: Rode NT55 - Versatile microphone with interchangeable omnidirectional and cardioid capsules suitable for diverse recording scenarios.
For Streaming/Interviews: Blue Yeti - Optimal for streaming and interviews, this microphone offers clear speech recording with multiple polar pattern options.
Premium Option: Schoeps CMC 1 MK 2 - A premium microphone renowned for superior sound quality, albeit lacking moisture resistance at its price point.
Conclusion:
The realm of omnidirectional microphones is vast and varied, brimming with potential to elevate your audio endeavors.
Through our extensive buyer's guide, we hope to have illuminated the path towards making an informed choice.
Remember, the best microphone isn't merely the most expensive or the most touted—it's the one that aligns seamlessly with your specific needs and budget.
Our six top picks are a testament to the diversity and depth this field offers.
As technology evolves, so will the world of microphones, but with this guide in your arsenal, you're well-equipped to make sound decisions for your audio adventures today and in the future.
Happy recording!
Help Support Acoustic Nature
If you enjoyed this post and would like to help support Acoustic Nature, please consider "buying me a coffee" or becoming a Patreon with the buttons below.
As a thank you for your support, Patreon supporters receive a copy of Field Recording For Beginners, exclusive access to the full Behind The Sounds video series, nature sound library downloads, and more.
If you are unable to support the site financially, please share this post with others, or leave a comment below letting me know you enjoyed this post! Both are free and help the website grow. Thank you ♫
Thanks for reading,
-Jared
Follow Me On:
Share this post and help the website grow: